Describe use cases for solutions
One of the basic design principles of the Common Data Service is the ability to customize the database to suit specific applications. The extensions that developers create, package, and deploy to the Common Data Service are called solutions. A solution consists of all the customizations made to the Common Data Service, including any modifications that developers might make to an existing solution. The entire solution is packaged as a single file that developers can distribute and import into other environments.
Solutions can contain a variety of components generated by the Power Platform tools, including Power Apps canvas apps and model-driven apps, Power Automate flows, custom connectors, and Common Data Service entities. However, solutions do not contain any business data.
Developers can create two types of solutions, as follows:
■ Unmanaged—Intended for development environments in which modifications are being made to the solution. Developers can export an unmanaged solution as either a managed or unmanaged solution. After a developer imports an unmanaged solution, deleting the solution causes the solution file to be deleted, but the customizations applied to the environment remain in place.
■ Managed—Intended for nondevelopment situations, such as test and production environments. Developers cannot export a managed solution or edit the components in a managed solution directly; they must first add the components to an unmanaged solution, which is editable. Deleting a managed solution causes all of the customizations included in the solution to be removed from the environment.
The typical progression is for developers to create and refine an unmanaged solution in a development environment and then export it as a managed solution for deployment in a test environment and later a production environment, as shown in Figure 2-8.
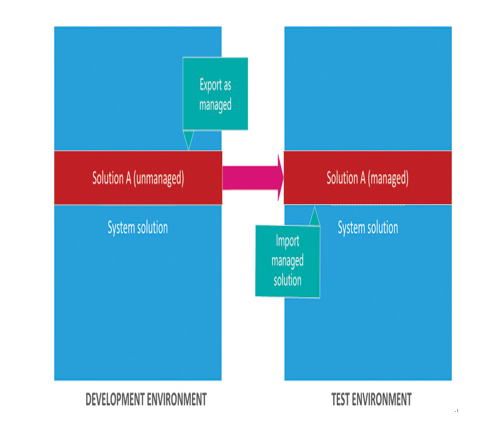
FIGURE 2-8 Development progression using unmanaged and managed solutions
To create a solution, a developer clicks the New solution button on the Solutions page in the Power Apps portal to open the dialog box shown in Figure 2-9. After the solution is created, the developer can then create components or add existing ones. Developers can employ solutions in a variety of use cases, including application lifecycle management and business process flows.
FIGURE 2-9 The New solution dialog box in the Power Apps portal
