Create powerful chatbots by using a guided, no-code graphical interface
Power Virtual Agents is a recent addition to the Power Platform toolkit that allows citizen developers to create customer service chatbots and embed them into websites using a simplified no-code interface. Chatbots, in this instance, are automated, text-based communication interfaces that use branching logic and artificial intelligence to communicate with online clients, ascertain their needs, and in some cases satisfy those needs by triggering flows that perform specific tasks.
When a developer creates a virtual agent and adds a default greeting, an authoring canvas appears like the one shown in Figure 1-29. By default, the bot’s standard Greeting topic is configured to respond to any one of 52 trigger phrases representing possible initial statements by the client with a standard greeting.
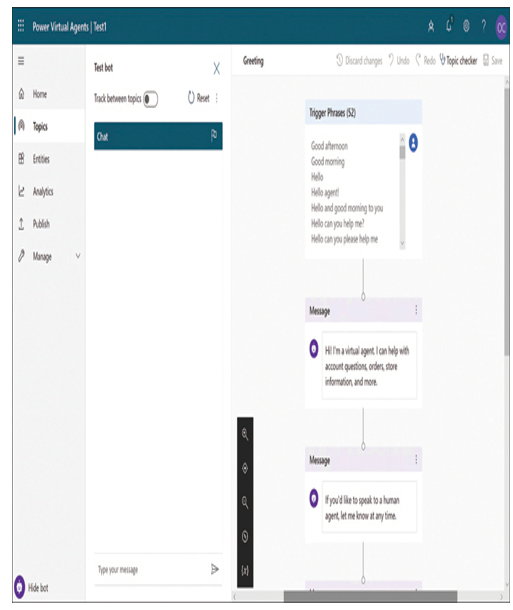
FIGURE 1-29 The Power Virtual Agents default greeting
The trigger phrases do not have to match the user’s input exactly. Power Virtual Agents uses a natural language understanding module to match variants of the trigger phrases with an appropriate response. The developer can add more trigger phrases and modify the bot’s greeting as needed.
To extend the conversation, the developer can create additional topics that ask the user questions, obtain information from the user, and take action based on that information. For example, Figure 1-30 shows a simple yes or no question and the branching logic that allows the developer to continue the conversation in different ways, depending on the response given.
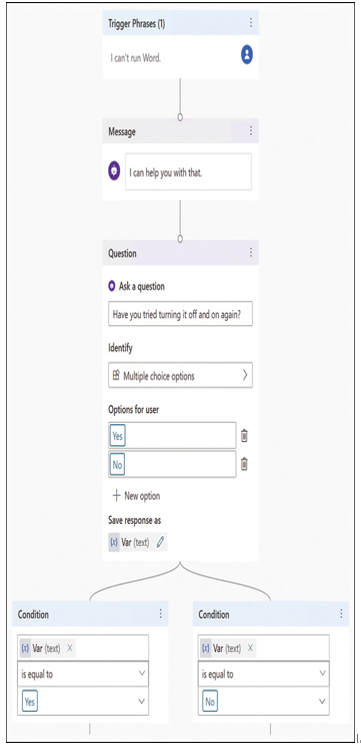
FIGURE 1-30 A Power Virtual Agents topic with branching logic
Power Virtual Agents can work together with Power Automate, so developers can create flows that perform tasks using information gathered from the user and integrate them into conversations. For example, in the case of a user wanting to check the status of an order, a topic in the bot’s conversation can prompt the user to specify an order number. Then, the bot can pass the order number to a flow that performs a database lookup and supplies information about the order back to the bot, which displays it to the user. For conversations that are unable to provide what the user needs, a topic can pass the user to a live agent.
